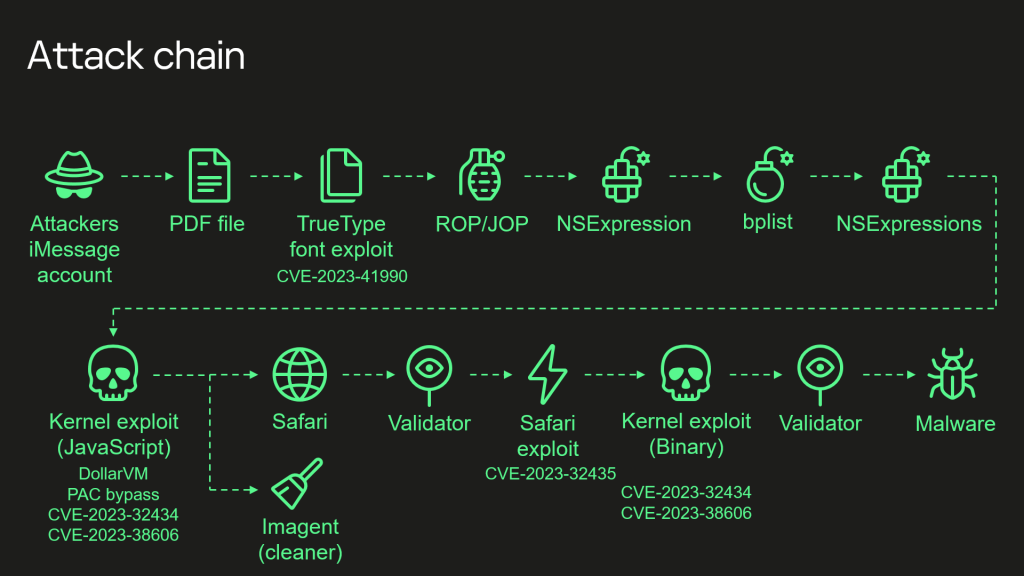
Brick-and-mortar companies, despite operating primarily in physical spaces, are not immune to the risk of data breaches. These breaches occur when sensitive customer information stored by the company is compromised or accessed by unauthorized parties. Common scenarios in which brick-and-mortar companies can experience data breaches include:
- Inadequate Security Measures: Many brick-and-mortar businesses collect and store customer data electronically, such as contact information, payment details, and purchase histories. If these businesses fail to implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect this data, such as encryption, firewalls, and access controls, they become vulnerable to breaches.
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: Retail stores and other brick-and-mortar establishments often use POS systems to process transactions. Hackers may target these systems to steal payment card information or install malware that captures sensitive data during transactions.
- Employee Error or Malfeasance: Human error or malicious actions by employees can also lead to data breaches. For example, an employee may inadvertently share sensitive customer information or fall victim to phishing scams, providing hackers with access to company systems.
- Physical Theft or Loss: Physical theft or loss of devices containing customer data, such as laptops, tablets, or paper records, can also result in data breaches. If these devices are not properly secured or encrypted, sensitive information can be accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Data breaches are unfortunately quite common, affecting brick-and-mortar companies of all sizes and industries. According to recent studies, data breaches in the retail sector alone accounted for a significant portion of all reported breaches globally. As businesses increasingly rely on digital systems to manage operations and customer interactions, the risk of data breaches continues to grow. Therefore, it is crucial for brick-and-mortar companies to prioritize cybersecurity measures and regularly assess and update their data protection practices to mitigate the risk of breaches and safeguard customer information.